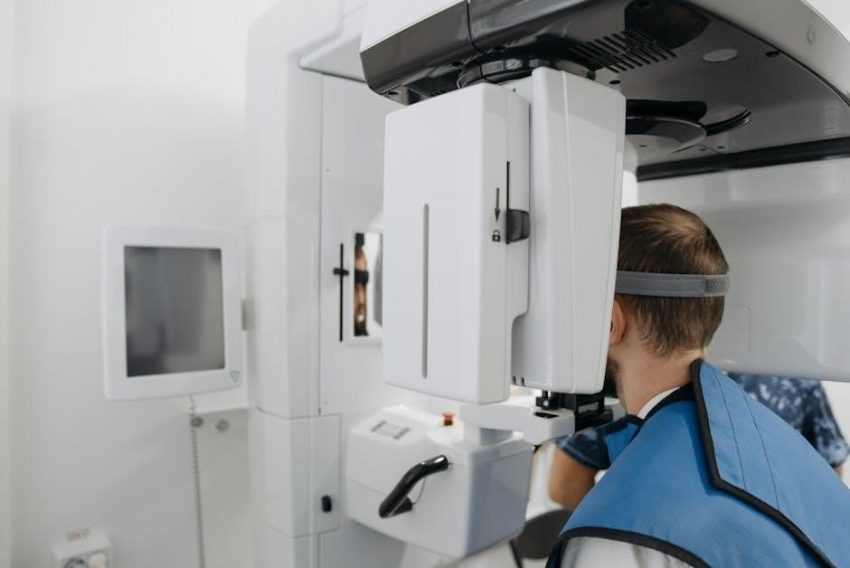
Veterinary dental X-ray positioning is essential for accurately diagnosing dental issues in pets. It involves precise techniques to capture clear images of teeth and surrounding structures‚ ensuring proper diagnosis and treatment planning. This guide provides a comprehensive approach to mastering X-ray positioning‚ emphasizing safety and accuracy for optimal patient care.
Importance of Dental X-Rays in Veterinary Medicine
Dental X-rays are crucial in veterinary medicine for diagnosing hidden dental issues‚ such as root fractures‚ bone loss‚ and abscesses‚ which are not visible during a routine oral exam. They provide detailed images of teeth and surrounding structures‚ enabling accurate diagnoses and effective treatment plans. X-rays also help identify asymptomatic conditions‚ ensuring early intervention and improving patient outcomes. Regular dental radiographs are essential for maintaining the oral health and overall well-being of pets.
Overview of the PDF Guide for Veterinary Dental X-Ray Positioning
This PDF guide provides a concise and detailed reference for veterinary teams‚ outlining essential techniques for dental X-ray positioning. It includes charts‚ tube head angles‚ and tips for capturing clear images of canine and feline teeth. The guide emphasizes proper positioning to minimize distortion and ensure accurate diagnoses. Designed for practical use‚ it serves as a handy tool for veterinarians and technicians‚ promoting efficient and effective dental radiography in clinical settings.
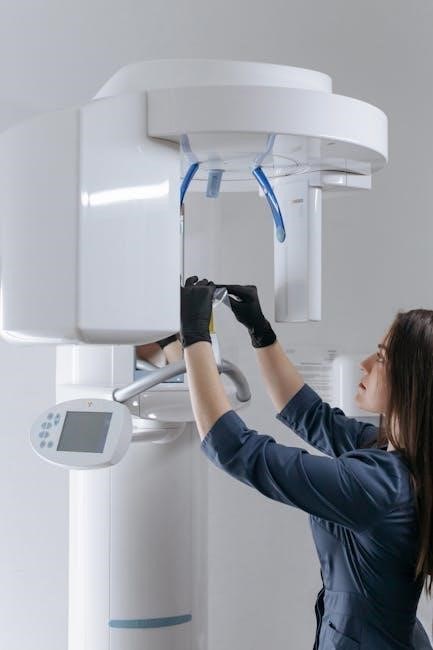

Basic Principles of Dental X-Ray Positioning
Dental X-ray positioning relies on the bisecting angle technique and proper beam alignment to ensure accurate‚ distortion-free images. This method minimizes anatomical overlap and enhances diagnostic clarity.
The Bisecting Angle Technique
The bisecting angle technique is a fundamental method in veterinary dental radiography. It involves positioning the X-ray beam perpendicular to the bisecting line between the tooth’s long axis and the sensor. This technique ensures that the resulting image is accurate in size and shape‚ minimizing distortion. Proper alignment is crucial for diagnosing dental issues effectively. The beam should be angled to avoid elongation or foreshortening of the tooth structure‚ providing a clear view of the root apices and surrounding bone. This method is widely recommended for its scientific accuracy and reliability in veterinary dental imaging.
Key Considerations for X-Ray Beam Alignment
Proper alignment of the X-ray beam is critical for obtaining clear and distortion-free images. The beam should be positioned perpendicular to the dental film or sensor to ensure accurate representation of tooth structures. Maintaining a consistent distance from the beam source to the patient helps prevent magnification errors. Additionally‚ the beam should be angled to avoid overlapping anatomical structures‚ ensuring that root apices and surrounding bone are visible for precise diagnosis. Proper alignment enhances image quality and diagnostic accuracy in veterinary dental radiography.

Standard Positioning Techniques for Canine and Feline Dental X-Rays
Standard positioning techniques ensure accurate imaging of dental structures in pets. Proper beam alignment and patient positioning are critical for clear radiographs‚ aiding in precise diagnoses and treatments.
Positioning for Mandibular Premolars and Molars
For mandibular premolars and molars‚ the X-ray beam should be aimed at a right angle to the bisecting angle‚ ensuring proper alignment. Canines require the beam to be angled slightly caudally‚ while felines need careful positioning due to smaller anatomy. The tube head should be 1-2 inches from the skin‚ and the sensor placed lingually to capture root apices. Adjustments may involve tilting the head or jaw for clear imaging‚ ensuring no distortion or overlap of structures.
Positioning for Maxillary Teeth and Canines
For maxillary teeth and canines‚ the X-ray beam is angled at 45-55 degrees to the bisecting angle‚ ensuring proper visualization of root structures. The tube head is positioned high and through the eye for molars‚ while canines require a slightly lower angle. The sensor should be placed palatally to avoid distortion. Adjustments may include tilting the head to align the beam correctly‚ ensuring clear imaging of the maxillary arch and avoiding superimposition of surrounding structures for accurate diagnosis.
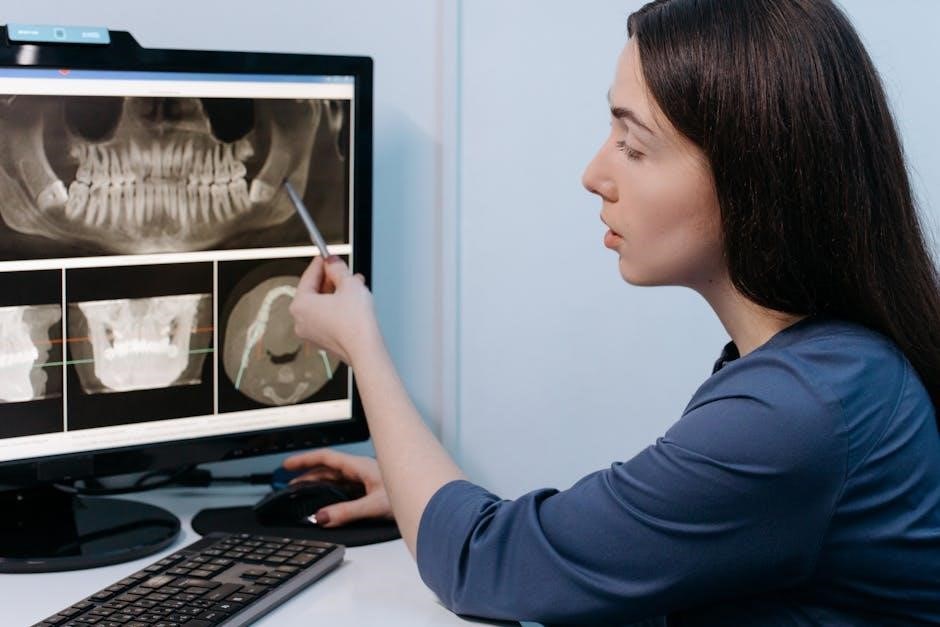
Common Positioning Errors and Corrections
Common errors include incorrect beam angles‚ leading to image distortion‚ and improper sensor placement‚ causing anatomy cutoff. Corrections involve adjusting tube head angles and ensuring proper alignment for clear imaging.
Understanding Image Distortion and Its Causes
Image distortion in veterinary dental radiography occurs when the X-ray beam is not properly aligned with the tooth and sensor. This can result in elongation or foreshortening of structures. Causes include improper beam angles and incorrect positioning. Accurate alignment is critical to ensure clear‚ undistorted images for proper diagnosis.
Distortion can also arise from improper sensor placement or uneven tooth-sensor alignment. Correcting these issues requires adjusting the tube head angle and ensuring the beam is perpendicular to the bisecting angle of the tooth. Proper positioning is essential for accurate imaging and effective diagnosis in veterinary dental care.
Adjusting Tube Head Angles for Accurate Imaging
Accurate imaging requires precise adjustment of the tube head angle to ensure the X-ray beam is properly aligned. The beam should be perpendicular to the bisecting angle of the tooth and sensor to avoid distortion. Proper alignment ensures clear‚ undistorted images for accurate diagnosis.
Adjustments may involve angling the beam to accommodate tooth location and anatomy. For example‚ a 20-degree caudal tilt is often used for mandibular imaging. Correct tube head positioning is critical for capturing detailed tooth and root structures in veterinary dental radiography.
Advanced Techniques for Challenging Cases
Advanced techniques address complex anatomical challenges‚ such as oblique views for bulla and mandible imaging‚ ensuring precise X-ray positioning for accurate diagnosis in difficult cases.
Oblique Views for Bulla and Mandible Imaging
Oblique views are essential for evaluating the bulla and mandible in veterinary dental imaging. To achieve this‚ rotate the mandible up or down based on the area of interest. Secure the endotracheal tube and tongue to prevent movement. Positioning the X-ray beam at a specific angle ensures clear visualization of the bulla and mandible‚ aiding in the diagnosis of fractures‚ infections‚ or dental anomalies. Proper alignment is critical for accurate imaging and patient safety.
Specialized Positioning for Frontal Bone and Maxilla
Specialized positioning for the frontal bone and maxilla requires precise alignment to capture clear images. Position the maxilla so the hard palate is perpendicular to the table surface‚ with nostrils pointing upward. Open the mouth to avoid superimposition of surrounding structures. The X-ray beam should be angled to ensure proper visualization of the frontal bone and maxilla‚ minimizing distortion. This technique is crucial for diagnosing issues like fractures or sinus infections‚ providing detailed images for accurate treatment planning.

Legal and Safety Considerations
Adherence to radiation safety protocols is critical in veterinary dental X-ray positioning. Ensure compliance with local and national standards to minimize radiation exposure‚ protecting both patients and staff.
Radiation Safety Protocols in Veterinary Practices
Radiation safety is paramount in veterinary dental X-ray positioning. Practices must follow strict protocols‚ including limiting exposure time‚ using lead aprons‚ and ensuring the X-ray head is 1-2 inches off the patient’s fur. Digital sensors reduce radiation doses‚ and staff should wear thyroid shields. Access to the X-ray area should be restricted during use‚ and regular equipment maintenance is essential to ensure safety and compliance with regulatory standards‚ protecting both patients and personnel.
Compliance with Veterinary Dental Radiography Standards
Compliance with veterinary dental radiography standards ensures accurate and safe imaging practices. Guidelines from organizations like the American Veterinary Dental College (AVDC) emphasize proper training‚ equipment calibration‚ and adherence to radiation safety protocols. Regular staff training and quality control measures are essential to maintain compliance. Proper record-keeping and informed consent processes also align with these standards‚ ensuring ethical and professional practice in veterinary dental radiography.
Case Studies and Practical Examples
Case studies offer practical insights into applying veterinary dental X-ray positioning techniques. Real-world examples demonstrate effective diagnosis and treatment of common dental issues in pets.
Real-World Applications of Dental X-Ray Positioning
Dental X-ray positioning is crucial for diagnosing conditions like tooth abscesses‚ fractures‚ and periodontal disease in pets. Properly angled images help identify root resorption or bone loss. Veterinarians use these radiographs to plan treatments‚ such as extractions or restorations. For example‚ a well-positioned X-ray can confirm whether a tooth is impacted or if a fracture extends to the pulp. Accurate imaging ensures precise care‚ improving patient outcomes and streamlining surgical procedures.
Interpreting Radiographs for Accurate Diagnosis
Interpreting dental radiographs requires careful examination of tooth structures and surrounding tissues. Look for signs of pathology‚ such as root resorption‚ bone loss‚ or fractures. Properly positioned images ensure clear visualization of apices and alveolar bone. Common errors‚ like missing apices or excessive black space‚ indicate misaligned X-ray beams. Adjusting tube head angles and sensor placement can correct these issues‚ enabling accurate diagnoses and effective treatment planning for pets.
Creating a PDF Cheat Sheet for Veterinary Dental X-Ray Positioning
A user-friendly PDF cheat sheet simplifies dental X-ray positioning for veterinary teams. It includes essential tube head angles‚ tips‚ and charts‚ serving as a quick reference guide.
Designing a User-Friendly Reference Guide
A well-designed reference guide for veterinary dental X-ray positioning should prioritize clarity and ease of use. Include detailed charts‚ tube head angles‚ and concise instructions for each tooth. Use a clean layout with visual aids like diagrams and labels to enhance understanding. Organize information logically‚ separating canine and feline specifics. Ensure the guide is compact yet comprehensive‚ making it a invaluable tool for quick consultations during procedures.
Including Essential Tube Head Angles and Tips
For clear imaging‚ include specific tube head angles for each tooth. Canines: 45-55 degrees‚ high and through the eye. Molars: 110-109 degrees‚ aligned through the infraorbital rim. Tips: Ensure the X-ray beam is perpendicular to the bisecting angle. Position the sensor securely against the tooth. Adjust angles to avoid distortion. Keep the X-ray head 1-2 inches off the skin for optimal focus. These details ensure accurate and distortion-free radiographs for precise diagnoses.
